China Electricity Council released the electricity operation profile for January-February: negative growth in power generation
Abstract In January and February, the national electricity supply and demand was generally loose. The electricity consumption of the whole society has been growing at a low rate, and the electricity consumption of the three industries and residents has increased rapidly. The growth of industrial electricity consumption has continued to be sluggish, and the electricity consumption of light and heavy industries has been negative. In addition to the positive growth of chemical power consumption, other high energy-consuming industries have used Electricity...
In January and February, the nation's electricity supply and demand was generally loose. The electricity consumption of the whole society has been growing at a low rate, and the electricity consumption of the three industries and residents has increased rapidly. The growth of industrial electricity consumption has continued to be sluggish, and the electricity consumption of light and heavy industries has been negative. In addition to the positive growth of chemical power consumption, other high energy-consuming industries have used The power consumption dropped sharply; the thermal power generation continued to grow negatively; other types of power generation increased rapidly; the hydropower utilization hours increased year-on-year, and the thermal power and nuclear power utilization hours decreased year-on-year; the national cross-regional and inter-provincial power transmission continued to grow at a low rate; The installed capacity increased year-on-year, and the installed capacity of thermal power plants increased significantly year-on-year. First, the whole society's electricity consumption is growing at a low rate, and the tertiary output and residents' electricity consumption are growing rapidly.
In January-February, the national total electricity consumption was 876.2 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 2.0%, and the growth rate dropped by 0.5 percentage points over the same period of the previous year.
In terms of industries, in January and February, the first industry used 1.17 billion kWh of electricity, up 6.7% year-on-year, accounting for 1.3% of the total electricity consumption in the whole society; the second industry used 591.5 billion kWh, down year-on-year. 2.1%, accounting for 67.5% of the total electricity consumption of the whole society, contributing -73.3% to the growth of electricity consumption in the whole society; 132.5 billion kWh of electricity consumption in the tertiary industry, up 11.9% year-on-year, accounting for the whole society The proportion of electricity is 15.1%, and the contribution rate to the growth of electricity consumption in the whole society is 82.2%; the electricity consumption of urban and rural residents is 140.5 billion kWh, up 11.8% year-on-year, accounting for 16.0% of the total electricity consumption of the whole society. The contribution rate to the growth of electricity consumption in the whole society is 86.8%.
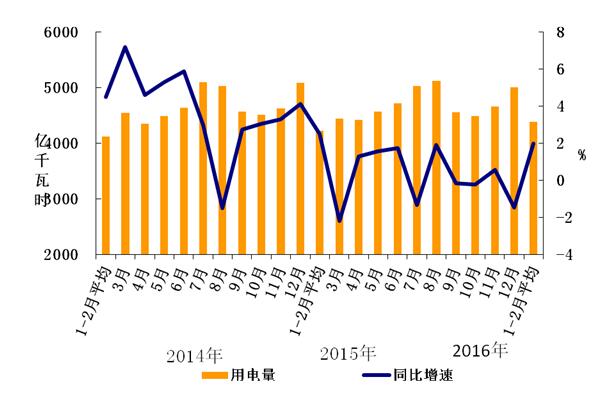
Figure 1: Electricity consumption and growth rate of the whole society in each month since 2014
In terms of regions, in the first two months, there were 17 provinces with a higher growth rate of electricity consumption than the national average (2.0%), followed by Tibet (10.9%), Xinjiang (10.2%), and Shaanxi (9.0%). ), Beijing (8.5%), Jiangxi (8.2%), Anhui (7.3%), Henan (6.4%), Hubei (6.0%), Shanghai (5.8%), Jiangsu (5.7%), Guangdong (4.3%), Hunan (3.5%), Heilongjiang (3.5%), Inner Mongolia (3.1%), Hainan (3.0%), Tianjin (2.5%) and Zhejiang (2.3%); there are 10 provinces with negative electricity consumption growth in the whole society, including The provinces with a speed below -5% are: Gansu (-8.5%), Ningxia (-13.5%) and Qinghai (-13.6%). Second, the growth of industrial electricity consumption continued to be weak, and the electricity consumption of light and heavy industries was negative.
In January-February, the national industrial electricity consumption was 579.2 billion kWh, down 2.0% year-on-year, and the growth rate dropped by 3.3 percentage points year-on-year, accounting for 66.1% of the total electricity consumption of the whole society, contributing to the growth of electricity consumption in the whole society. It is -70.1%. Among them, light industry electricity consumption was 98.5 billion kWh, down 0.8% year-on-year, and the growth rate dropped 11.2 percentage points over the same period of the previous year; heavy industry electricity consumption was 480.7 billion kWh, down 2.3% year-on-year, and the growth rate dropped 1.8 times compared with the same period of the previous year. Percentage points.
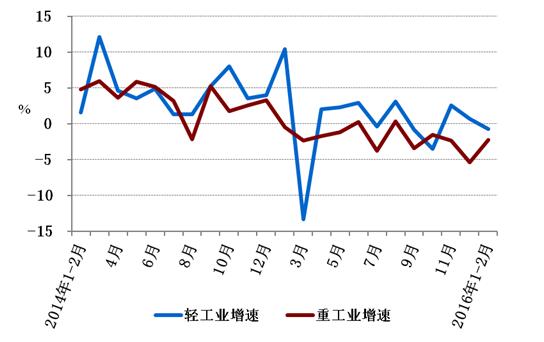
Figure 2: Monthly growth rate of light and heavy industry electricity consumption since 2014
In January-February, the national manufacturing power consumption was 431.2 billion kWh, down 6.1% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 10.4 percentage points lower than the same period of the previous year. 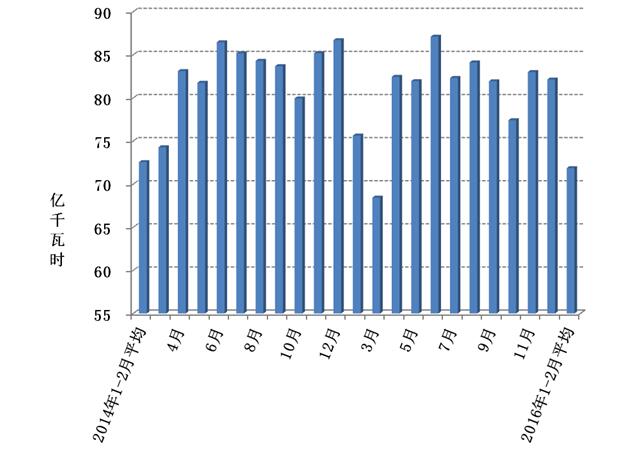
Figure 3: Average daily electricity consumption in manufacturing months since 2014
3. In addition to the positive growth of chemical power consumption, the electricity consumption of other high-energy-consuming industries fell sharply. In January and February, the total electricity consumption of chemical raw materials, non-metallic mineral products, ferrous metal smelting and non-ferrous metal smelting in the four high-energy industries totaled 244.1 billion kWh, a year-on-year decrease of 10.1%, and the growth rate dropped by 10.6 percentage points year-on-year; Electricity consumption accounts for 27.9% of the total electricity consumption of the whole society, and the contribution rate to the growth of electricity consumption in the whole society is -159.3%. Among them, the chemical industry used 67.9 billion kWh of electricity, up 3.3% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 0.7 percentage points higher than the same period of the previous year; the building materials industry used 37.2 billion kWh, down 12.0% year-on-year, and the growth rate dropped compared with the same period of last year. 17.8 percentage points; the ferrous metal smelting industry used 67.1 billion kWh of electricity, down 18.0% year-on-year, and the growth rate dropped by 12.4 percentage points over the same period of the previous year; the non-ferrous metal smelting industry was 71.9 billion kWh, down 11.8% year-on-year. The year-on-year decline was 15.3 percentage points.
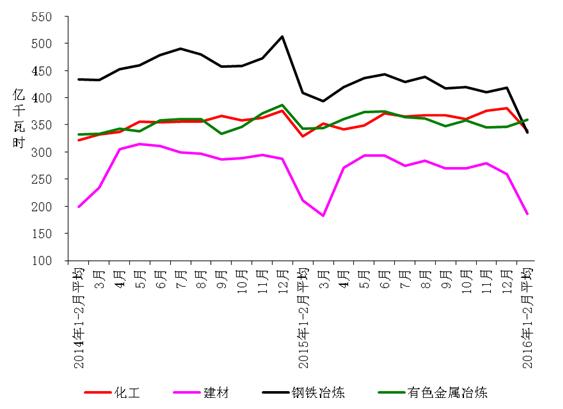
Figure 4: Electricity consumption in key industries in the month since 2014
4. Thermal power generation continued to grow negatively, and other types of power generation grew rapidly. As of the end of February, the installed capacity of power plants with a capacity of 6,000 kW and above was 1.49 billion kilowatts, a year-on-year increase of 11.8%. Among them, hydropower 280 million kilowatts, thermal power 1 billion megawatts, nuclear power 28.14 million kilowatts, grid-connected wind power 133.3 million kilowatts. In January-February, the power generation capacity of power plants above designated size was 870.2 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 0.3%, and the growth rate was 1.6 percentage points lower than the same period of the previous year.
In January-February, the hydropower generation capacity of power plants above designated size reached 128.9 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 22.6%, and the growth rate increased by 10 percentage points year-on-year. The top three provinces in China's hydropower generation are Sichuan (33.2 billion kWh), Yunnan (22.2 billion kWh) and Hubei (14.6 billion kWh), and their combined hydropower generation accounts for 54.3% of the country's hydropower generation. The speeds were 18.8%, 11.8% and 12.4%, respectively.
In January-February, the thermal power generation capacity of power plants above designated size nationwide was 678.6 billion kWh, down 4.3% year-on-year, a decrease of 3.5 percentage points over the same period of the previous year. Among the provinces, only Xinjiang, Anhui, and Hubei grew rapidly (17.5%, 11.0%, and 10.8%), and the thermal power generation in 20 provinces experienced negative growth. Fujian (-39.5%) and Yunnan (-47.1%) fell close to or exceeded 40%.
In January-February, the national nuclear power generation capacity was 28.5 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 23.1%, a decrease of 7.9 percentage points over the same period of the previous year.
In January-February, the power generation capacity of wind farms with a capacity of 6,000 kW and above was 34.8 billion kWh, a year-on-year increase of 21.9%, which was flat compared with the same period of the previous year.
5. The utilization hours of hydropower increased year-on-year, and the decrease in the utilization hours of thermal power and nuclear power increased year-on-year.
In January-February, the cumulative average utilization hours of power generation equipment in the country was 575 hours, a year-on-year decrease of 54 hours, and the decrease was 15 hours.
In terms of types, in January and February, the average utilization time of hydropower equipment in the country was 445 hours, a year-on-year increase of 72 hours; of the seven provinces with hydropower installed capacity exceeding 10 million kilowatts, only Qinghai fell by 50 hours, and the remaining provinces increased. Among them, Hunan grew by 289 hours, Guizhou increased by 121 hours, and Guangxi increased by 100 hours. The average utilization rate of thermal power equipment in the country was 656 hours, down 83 hours year-on-year, and the growth rate was 31 hours longer than that in the same period of 2015. The hours of utilization in Beijing, Hebei, Jiangsu and Anhui were close to or exceeded 800 hours; compared with the same period of last year, there were 25 The utilization hours of thermal power in the province decreased year-on-year, of which Sichuan, Tibet, Qinghai and Fujian fell more than 300 hours. The average utilization time of nuclear power equipment in the country was 1025 hours, a drop of 68 hours. The average utilization rate of wind power equipment in the country was 263 hours, down 39 hours year-on-year.
6. National cross-regional and inter-provincial power transmission maintained a low growth rate
In the first two months of this year, the nationwide cross-regional power transmission reached 42.2 billion kWh, an increase of 3.4% year-on-year. Among them, North China sent to China (UHV) 1.4 billion kWh, down 17.0%; North China sent East China 2.4 billion kWh, down 0.9%; Northeast to North China 3.7 billion kWh, up 3.3%; East China sent Huazhong 0 billion Kilowatt hours, a year-on-year increase of -99.9%; Huazhong sent East China 3.3 billion kWh, an increase of 121.4%; Huazhong sent a southern 2.4 billion kWh, down 17.1%; Northwest to North China and Central China totaled 13.3 billion kWh, an increase of 13.9% The southwest sent East China 8.4 billion kWh, an increase of 3.7%.
In the first two months of this year, the provinces sent a total of 121.6 billion kWh of electricity, an increase of 3.8%. Among them, Inner Mongolia sent 17.7 billion kWh of electricity, down 9.9% year-on-year; Shanxi delivered 11.5 billion kWh, down 4.7% year-on-year; Sichuan sent 10.8 billion kWh, up 2.6% year-on-year; Guizhou sent 9.8 billion kWh, An increase of 10.9%; Anhui sent 9.4 billion kWh of electricity, an increase of 37.2%; Hubei sent 9.2 billion kWh, an increase of 20.9%; Yunnan sent 6.6 billion kWh, an increase of 24.0%; Hebei sent 6.3 billion kWh , a year-on-year increase of 11.4%; Xinjiang sent 5.2 billion kWh of electricity, an increase of 15.3%.
7. The newly installed capacity of infrastructure construction increased year-on-year, and the installed capacity of thermal power plants increased significantly year-on-year.
In January-February, the national infrastructure construction capacity increased by 22.28 million kilowatts, which was 8.86 million kilowatts more than the same period of the previous year. Among them, hydropower 990,000 kilowatts, thermal power 13.95 million kilowatts, nuclear power 2.27 million kilowatts, wind power 1.6 million kilowatts, solar energy 3.48 million kilowatts, hydropower compared with the same period last year, less than 400,000 kilowatts; thermal power, nuclear power, wind power, solar energy, respectively, more than the same period last year 608, 118, 59 and 1.42 million kilowatts.
8. The investment in power supply decreased year-on-year, and the investment in power grids increased year-on-year.
In the first two months of this year, the power generation project of major power generation enterprises nationwide completed 31.6 billion yuan, a decrease of 21.5% over the same period of the previous year. In the completion of investment in power supply, hydropower completed investment of 8.4 billion yuan, down 12.7% year-on-year; thermal power completed investment of 8.6 billion yuan, down 43.5% year-on-year; wind power completed investment of 6.8 billion yuan, down 19.6% year-on-year; nuclear power completed investment of 5.3 billion yuan, Decreased by 4.0%. The investment in clean energy such as hydropower, nuclear power and wind power accounted for 72.9% of the investment in power supply, an increase of 10.6 percentage points over the same period of the previous year.
In January-February, the national grid project completed an investment of 44.9 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 35.8%.
Source: China Electricity Council Planning and Development Department
KMP Parts,KMP Engine Parts,KMP Auto Parts,KMP Excavator Parts
JINING SHANTE SONGZHENG CONSTRUCTION MACHINERY CO.LTD , https://www.sdkomatsudozerparts.com